
Cloud computing generated 127 billion dollars in 2016 and by 2020 it could be 500 billion dollars
Cloud computing is the delivery of computing services. It includes servers, storage, networking, software applications and more over the Internet. Cloud computing is not a technology. It is a computing model. All the servers, applications and other IT assets are made available to end users via the Internet. It allows IT industries to buy only the type and amount of computing services that they need. Customers using cloud don’t have to give their own IT resources to be managed. Instead, they plug into the “cloud” for infrastructure as services, platform as services or software as services. It allows them to treat the “cloud” as their internal data center or their server providing them same and often more advanced functions.
Where exactly is this cloud?
So, to answer this question in simpler words, it is somewhere at the other end of your internet connection where you store your files. Also, it can be accessed from anywhere in the world. This could be a big deal for you, primarily because of three reasons:
- Little to no maintenance and administration of any infrastructure is required
- It is virtually infinite so you won’t run out of storage
- Cloud-based applications can be accessed from anywhere, using a device which can connect to the internet.
Cloud Computing term in itself is very broad. Therefore, the services it offers has been divided into three different models:
- SaaS
- PaaS
- IaaS
SaaS (Software as a Service)
In this service, the Cloud Provider leases applications and software which are owned by them to its client. The client can access these softwares on any device which is connected to the Internet using tools such as a web browser, a mobile app etc.
For example, Salesforce.com provides the CRM (Customer Relation Manager) on a cloud infrastructure to its clients. It charges them for it, but the software is owned by the Salesforce company only.
PaaS (Platform as a Service)
Here, the Cloud service providers offer the ability to deploy applications created by its clients using programming languages and other API tools. The customer is provided with an underlying architecture including operating systems, storage etc.
This service model is best suited for the developers. They get a platform for developing applications, like Gmail, Grammarly.com etc. The cloud provides an easy to test and deploy service which otherwise is a tedious task.
IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service)
In this service, the Cloud Provider offers the customer with virtual machines and other resources as a service. It is the lowest level of cloud service which offers maximum control. They abstract the user from the physical machine, location, data partitioning etc. You don’t have to worry about the physical machine or the networking of the system on which the OS is installed.
For example, Amazon Web Services (AWS) offers IaaS with AWS EC2.
The diagram below, summarizes the differences b/w IaaS, PaaS and SaaS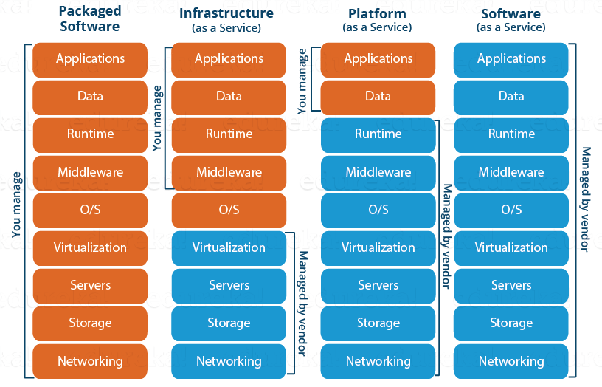
We now know about the service models. Once you choose a service and offer your own cloud-based product or service, next comes deployment. Let us now discuss the deployment models:
- Public Cloud
- Private Cloud
- Hybrid Cloud
Public Cloud
In a public cloud deployment model, the services which are deployed are open for public use and generally public cloud services are free. Technically there may be no difference between a public cloud hosting and a private cloud, but the security parameters are very different, since the public cloud is accessible by anyone so there is a more risk factor involved with it.
Private Cloud
A private cloud is operated solely for a single organization. It can be done by the same organization or any third-party. But usually the costs are high when you are using your own cloud since the hardware would be updated periodically, security also has to be kept in check since new threats come up every day.
Hybrid Cloud
A hybrid cloud consists of the functionalities of both private and public cloud. How?
For example, a research company, will have some published data and also, data which is still in the research phase. A cloud provider may deliver greater features and stronger security features but then it is still open to the public, consequently open to cyber-attacks. To address this risk, they can keep the data which is still in R&D, in their company’s servers whose access is controlled by them. Later, they can publish their data on the public platform. This type of arrangement is called a hybrid cloud.
Having learned the insights of cloud computing, you now can look at the cloud as an individual or for your business productivity.
Conclusion
Those of us who work in small to medium organizations, we use the internet on a regular basis. We use cloud services like Google Drive, DropBox, Gmail etc. for our personal use. But, for organizations and businesses, it is an entirely different picture. For them, the cloud is SaaS where they might want to use their software on the cloud. They may use it as PaaS where they might want to build an app on an environment which is provided by the cloud. Also, cloud services can be an Infrastructure wherein they can rent entire VMs and configure it in their own way. Ultimately, to the organizations, cloud means business productivity and profitability.
Contact us today to learn about Bleuwire™ services and solutions in how we can help your business.





